USA grapples with high drugs costs
 Volume 386, Number 10009
Volume 386, Number 10009
28 November 2015
WORLD REPORT More Americans are getting health insurance, including coverage for prescription drugs, but high prices may make them inaccessible. Susan Jaffe, The Lancet’s Washington correspondent, reports.
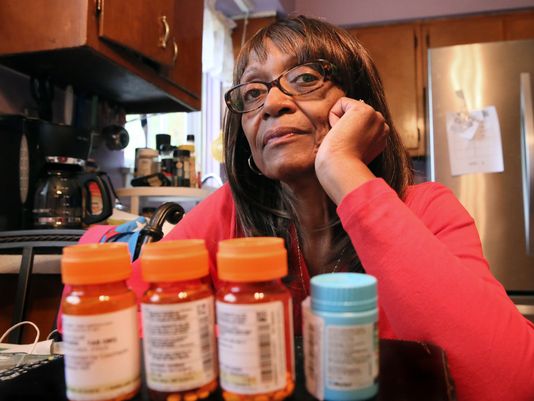
Patients in the USA pay more for prescription drugs than almost anywhere else in the world, forcing as many as one in four who can’t afford the high prices to go without their medicine last year, according to a Kaiser Family Foundation survey. So even though more Americans have health insurance, the new therapies and cures that can prevent more expensive health complications might be out of reach.
After several well-publicised, huge spikes in drug prices—including Turing Pharmaceutical’s increase for pyrimethamine (marketed as Daraprim) from US$13·50 to $750 a pill—the problem is drawing unprecedented attention from nearly every quarter: the Obama Administration, Congress, state officials, health insurance companies, drug makers, as well as the physicians and their patients who have clamoured for help for years. It also surfaced during this month’s Democratic presidential debate.
Heather Block, a patient advocate from Delaware who spoke at a day-long pharmaceutical forum hosted by the US Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) earlier this month, pays $9800 a month for the drugs she takes to treat breast cancer that has spread to her liver and lungs. Although she has Medicare coverage, she is still responsible for a share of her medical expenses. “Innovation is meaningless if nobody can afford it”, she said. “I still face financial insecurity and eventually bankruptcy—if I live that long.” [Continued here ]
Can you hear me now?
The President’s science advisors say innovative technology can provide low-cost alternatives to pricey hearing aids.
Susan Jaffe | Washington Correspondent for The Lancet | 11th November 2015
Almost  30 million Americans over 60 years old have difficulty hearing, but less than a third can afford hearing aids, according to a report to President Barack Obama by his Council of Advisors on Science and Technology two weeks ago. Even though hearing loss is often part of the natural aging process, the council did not recommend that Medicare, pay for hearing aids, which can cost an average of $5,000 to $6,000 for a pair. [Continued here]
30 million Americans over 60 years old have difficulty hearing, but less than a third can afford hearing aids, according to a report to President Barack Obama by his Council of Advisors on Science and Technology two weeks ago. Even though hearing loss is often part of the natural aging process, the council did not recommend that Medicare, pay for hearing aids, which can cost an average of $5,000 to $6,000 for a pair. [Continued here]
Don’t Just Renew Your Medicare Plan. Shopping Around Can Save Money.
By Susan Jaffe | October 15, 2015 | Kaiser Health News in collaboration with Money magazine
Ten years after a prescription drug benefit was added to Medicare, 39 million older or disabled Amer icans have coverage to help pay for their medicine, including most of the 17 million with private insurance policies known as Medicare Advantage, an alternative to traditional Medicare.
icans have coverage to help pay for their medicine, including most of the 17 million with private insurance policies known as Medicare Advantage, an alternative to traditional Medicare.
The annual enrollment period for these private drug and Advantage plans for 2016 starts Thursday and runs through Dec. 7.
period for these private drug and Advantage plans for 2016 starts Thursday and runs through Dec. 7.
It pays to shop around. The monthly cost is increasing an average 26 percent for UnitedHealthcare’s AARP MedicareRx Saver Plus while the First Health Value Plus plan
is dropping an average 13 percent, according to an analysis of the 10 most popular drug plans by Avalere Health, a research firm.
Some actual costs may be even more dramatic. In Albany, N.Y., the price of a Cigna-HealthSpring drug plan is going up 36 percent, according to the StateWide Senior Action Council, a New York consumer group. [More in Kaiser Health News or Money magazine]
Medicare Advantage Plans Need Tougher Oversight, GAO Says
| Connecticut Health Investigative Team Writer | October 5, 2015
Federal investigators have found that Medicare officials rarely enforce rules for private insurance plans intended to make sure beneficiaries will be able to see a doctor when they need care.
It’s a problem many Connecticut seniors know too well. In 2013, UnitedHealthcare, the nation’s largest health insurance company, dropped hundreds of health care providers from its  Connecticut Medicare Advantage plan, including 1,200 doctors at the Yale Medical Group and Yale-New Haven Hospital. Medicare Advantage beneficiaries scrambled to find new insurance or new doctors while the Fairfield and Hartford counties medical associations went to court to try to stop the terminations.
Connecticut Medicare Advantage plan, including 1,200 doctors at the Yale Medical Group and Yale-New Haven Hospital. Medicare Advantage beneficiaries scrambled to find new insurance or new doctors while the Fairfield and Hartford counties medical associations went to court to try to stop the terminations.
The report by the Government Accountability Office, the investigative arm of Congress, said that Medicare did not check provider networks to ensure that doctors were available to beneficiaries and cited Connecticut as a “case study” in what can go wrong.
The GAO report shows that Medicare “was not verifying network adequacy. That’s their job and they abdicated that responsibility,” said U.S. Rep. Rosa DeLauro, D-New Haven, who requested the investigation along with other members of the Connecticut congressional delegation. MORE
To Sell Medical Students On Joys Of Geriatrics, Send In 90-Year-Olds
By Susan Jaffe | Kaiser Health News | September 23, 2015 | This KHN story also ran in ![]()
When doctors told Robert Madison that his wife had dementia, they didn’t explain very much. His successful career as an architect hardly prepared him for what came next.
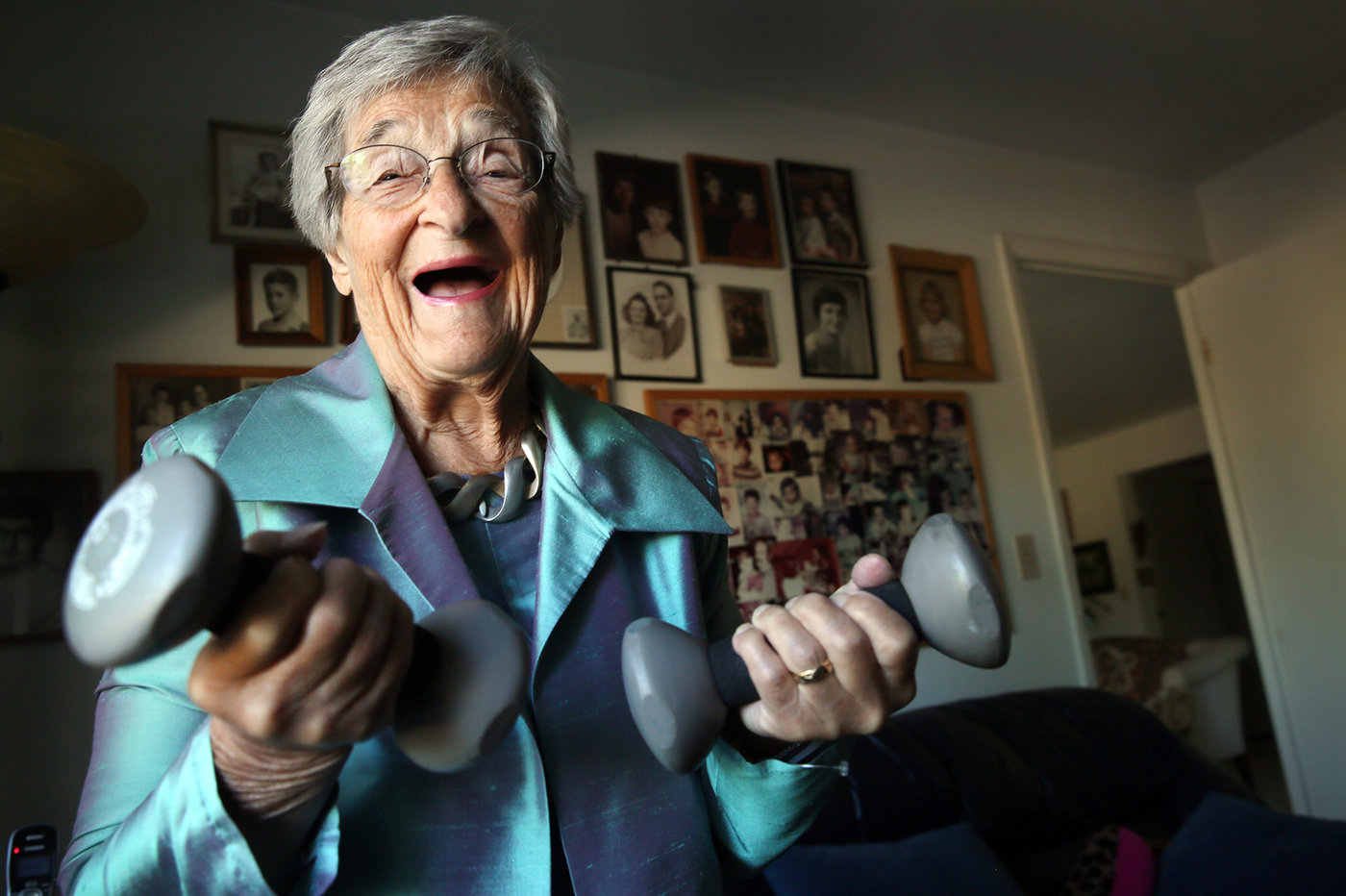

Belle Likover, a 95-year-old retired social worker, told Case Western Reserve medical students that growing old gracefully is all about being able to adapt to one’s changing life situation, including health challenges. Lynn Ischay/Kaiser Health News
“A week before she passed away her behavior was different, and I was angry because I thought she was deliberately not doing things,” Madison, now 92, told a group of nearly 200 students at Case Western Reserve School of Medicine in Cleveland. “You are knowledgeable in treating patients, but I’m the patient, too, and if someone had said she can’t control anything, I would have been better able to understand what was taking place.”
Belle Likover recounted for the students how she insisted when her husband was dying of lymphoma that doctors in the hospital not make decisions without involving his oncologist. “When someone is in the hospital, they need an advocate with them at all times,” said Likover, who turns 96 next month. “But to expect that from families when they are in crisis is expecting too much. The medical profession has to address that.”
Madison and Likover were among six people all over the age of 90 invited to talk to second-year medical students this month. The annual panel discussion, called “Life Over 90,” is aimed at nudging students toward choosing geriatric medicine, the primary care field that focuses on the elderly. It is among the lowest-paid specialties, and geriatricians must contend with complex cases that are time consuming and are often not reimbursed well by Medicare or private insurance. And their patients can have diseases that can only be managed but never cured [Continued at Kaiser Health News and at NPR]
USA gears up for next round of enrolment under the ACA
WORLD REPORT As enrolment begins for the Affordable Care Act’s health insurance, officials cut estimates of how many Americans will get coverage. Susan Jaffe, The Lancet’s Washington correspondent, reports.
The past 2 years of President Barack Obama’s landmark health insurance programme haven’ t been easy—surviving two Supreme Court challenges, nearly done-in by embarrassing technical glitches, and more than 50 congressional votes attempting to dismantle it. But its troubles are not yet over: enrolling new beneficiaries “is going to be tougher than last year”, warned Health and Human Services (HHS) Secretary Sylvia Mathews Burwell.
t been easy—surviving two Supreme Court challenges, nearly done-in by embarrassing technical glitches, and more than 50 congressional votes attempting to dismantle it. But its troubles are not yet over: enrolling new beneficiaries “is going to be tougher than last year”, warned Health and Human Services (HHS) Secretary Sylvia Mathews Burwell.
Burwell and other Obama Administration officials are damping down enrolment expectations just days before the 3-month sign-up period for 2016 coverage begins on Nov 1. [Continued here ]
End in sight for revision of US medical research rules
 Volume 386, Number 10000
Volume 386, Number 10000
26 September 2015
WORLD REPORT End in sight for revision of US medical research rules US health officials expect to update 25-year-old regulations on human participation in research by the end of next year. Susan Jaffe, The Lancet’s Washington correspondent, reports.
After proposing massive changes 4 years ago to rules first issued in 1991 protecting people participating in research studies, federal health officials produced yet another revision earlier this month and say the effort to update the rules is on a fast track.
The revolution in science, technology, medicine, and public involvement that has transformed biomedical research over the past 25 years might be sufficient reason for the latest update, a daunting task that began in 2009, shortly after Barack Obama became president. But now there’s another factor driving the effort. [Continued here]
U.S. House of Representatives possibly “injured” by ACA spending, judge OKs lawsuit
Susan Jaffe | Washington Correspondent for The Lancet | 15th September 2015
A new threat to the Affordable Care Act emerged last week when a federal judge decided to allow an unusual lawsuit by Republicans in the U. S. House of Representatives against President Barack Obama, claiming that his Administration violated the U. S. Constitution by spending billions of dollars for the Affordable Care Act that Congress did not approve. [Continued here] House of Representatives 091515
Billions served but Cleveland Clinic says no thanks to McDonald’s
Susan Jaffe | Washington Correspondent for The Lancet 9th September 2015
McDonald’s, the giant fast-food restaurant chain, has been adding healthy options to its menu of burgers, fries and shakes, but the new choices are too little, too late for the Cleveland Clinic.
After 20 years of serving patients, visitors, and Clinic employees in Cleveland, Ohio, the restaurant’s last day will be September 18. The world renowned hospital is not renewing its contract with McDonald’s.
“As a part of Cleveland Clinic’s commitment to health and wellness, we have made a number of changes across our health system over the past ten years that promote healthy food choices, exercise, and a smoke free environment,” said Eileen Sheil, the Clinic’s executive director for corporate communications, explaining why McDonald’s had to go. [Continued here]
Home-Care Workers
![]()
Susan Jaffe | Washington Correspondent for The Lancet | 28 August 2015
Home-care workers are excluded from the federal law requiring most employees to receive a minimum wage—currently $7·25 an hour—and 150% of that pay when they work overtime. After 40 years, the US Department of Labor (DOL) issued rules eliminating that exemption. The new rule was supposed to take effect last January but it was blocked by a lawsuit filed by associations representing companies that hire these workers. [Continued here.] [with video of Illinois Congresswoman Jan Schakowsky shadowing home-care worker Gilda Pipersburgh]
Congressional showdown threatens NIH funding boost
 Volume 386, Issue 9996, 29 August 2015
Volume 386, Issue 9996, 29 August 2015
WORLD REPORT Bills providing extra funding for the National Institutes of Health while cutting other programmes could a face presidential veto. Susan Jaffe, The Lancet’s Washington correspondent, reports.
After years of mostly stagnant funding for the US National Institutes of Health (NIH), two powerful congressional committees that control government spending have approved separate budget bills containing record increases for the agency.
But last month, President Barack Obama’s Office of Management and Budget director Shaun Donovan wrote to the chairman of the Senate Committee on Appropriations warning that he expects the president to veto its bill. Among other reasons, Donovan said it “drastically” cuts money for public health programmes including Medicare for the elderly and Medicaid, serving low-income Americans. And it would deny funds for operating the health insurance exchanges essential to the president’s signature health reform law, the Affordable Care Act. [Continued in full text or PDF ]
Clean Power Plan
Susan Jaffe | Washington Correspondent for The Lancet 25th August 2015
Before President Barack Obama’s Clean Power Plan can inspire other nations to control greenhouse gases by following the USA’s lead in dramatically reducing carbon emissions, the Administration has to convince West Virginia—and at least 15 other skeptical states. [Continued here]
21st Century Cures
 12 August 2015
12 August 2015
A dispatch from our Washington correspondent on the sluggish progress of the 21st Century Cures Act.
Republicans and Democrats in the U.S. House of Representatives last month overwhelmingly passed the 21st Century Cures Act aimed at speeding up drug development. But the Senate is not expected to vote on its version until next year.
More than 80 percent of the House backed the legislation after it was unanimously — a word rarely heard on Capitol Hill — approved by the House Committee on Energy and Commerce. In the process, the bill was revised to address concerns that drug approvals would happen a little too quickly, circumventing safety and efficacy standards. [Continued here]
50 Years of Medicare
 Volume 386, Issue 9992, 1 August 2015
Volume 386, Issue 9992, 1 August 2015
WORLD REPORT In July, 1965, Medicare, America’s landmark national health insurance programme, became law. Today, it covers 55 million people. Susan Jaffe, The Lancet’s Washington correspondent, reports.